앞서 JPA(Java Persistence API)의 간략하게 개념과 적용하는 것에 대해 설명하였다. 이번엔 JPA에서 중요한 개념인 EntityManger와 Persistence Context에 대해서 알아보았다.
Entity
Entity는 데이터베이스의 테이블을 모델링한 클래스로서 본질적인 객체를 뜻한다. Entity 는 Web Application Layer에서 Domain Layer에 해당하며, 객체 지향 중심으로 설계하는 애플리케이션에서 데이터베이스의 테이블을 객체로 다루기 위해 Domain 객체로 표현한다. 그리하여 Domain을 Entity로 지정하면, 애플리케이션 로직은 Domain을 대상으로 DB에 반영할수 있게된다.
다음 코드에서 Member 도메인 클래스를 @Entity annotation으로 지정하였다.
import jakarta.persistence.*;
@Entity
public class Member {
// Private ID (IDENTITY: DB에서 PK 자동 생성)
@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
// DB Column명 설정
@Column(name = "username")
private String name;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
jakarta.persistence는 Jakarta Persistence API(JPA)를 나타내며, 자바 객체와 관계형 데이터베이스 테이블의 매핑을 관리하는 표준 API이다. @Entity는 JPA의 annotation이다.
엔티티에서 id를 @Id(Primary Key)로 지정하고 DB에서 id가 자동 생성되도록 @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)로 지정하면, member 테이블에 행이 추가될때마다 id가 1씩 증가되면서 저장된다. 그리고 필드명과 다르게 테이블 column명으로 적용하고 싶다면, @Column(field_name = "column_name") 이렇게 설정할수 있다.
EntityManager
데이터베이스에서 트랜잭션이 커밋되어야 DB에 반영되기 때문에, entity 객체를 즉각적으로 DB에 반영하는 것은 불가하다. 그리하여 entity 객체의 생성부터 DB 동기화까지의 상태를 관리하는 것이 EntityManager 구현체이다. 이는 entity 객체와 DB 테이블은 서로 연결되어 있는 상태라고 볼수 있으며, EntityManager 구현체는 트랜잭션 동안의 entity 객체와 DB 테이블간의 세션(Session)을 뜻한다. 이 세션은 트랜잭션을 마치기전까지 entity와 DB 테이블간의 상태를 유지해야되므로 stateful session이다. Stateful Session 관련한 내용은 [JDBC] Connection에 대한 고찰에서 이해할수 있을것이다.
그래서 JPA의 구현체 Hiberante ORM에서 EntityManager 인터페이스를 extends하여 Session 인터페이스로 표현하였다.
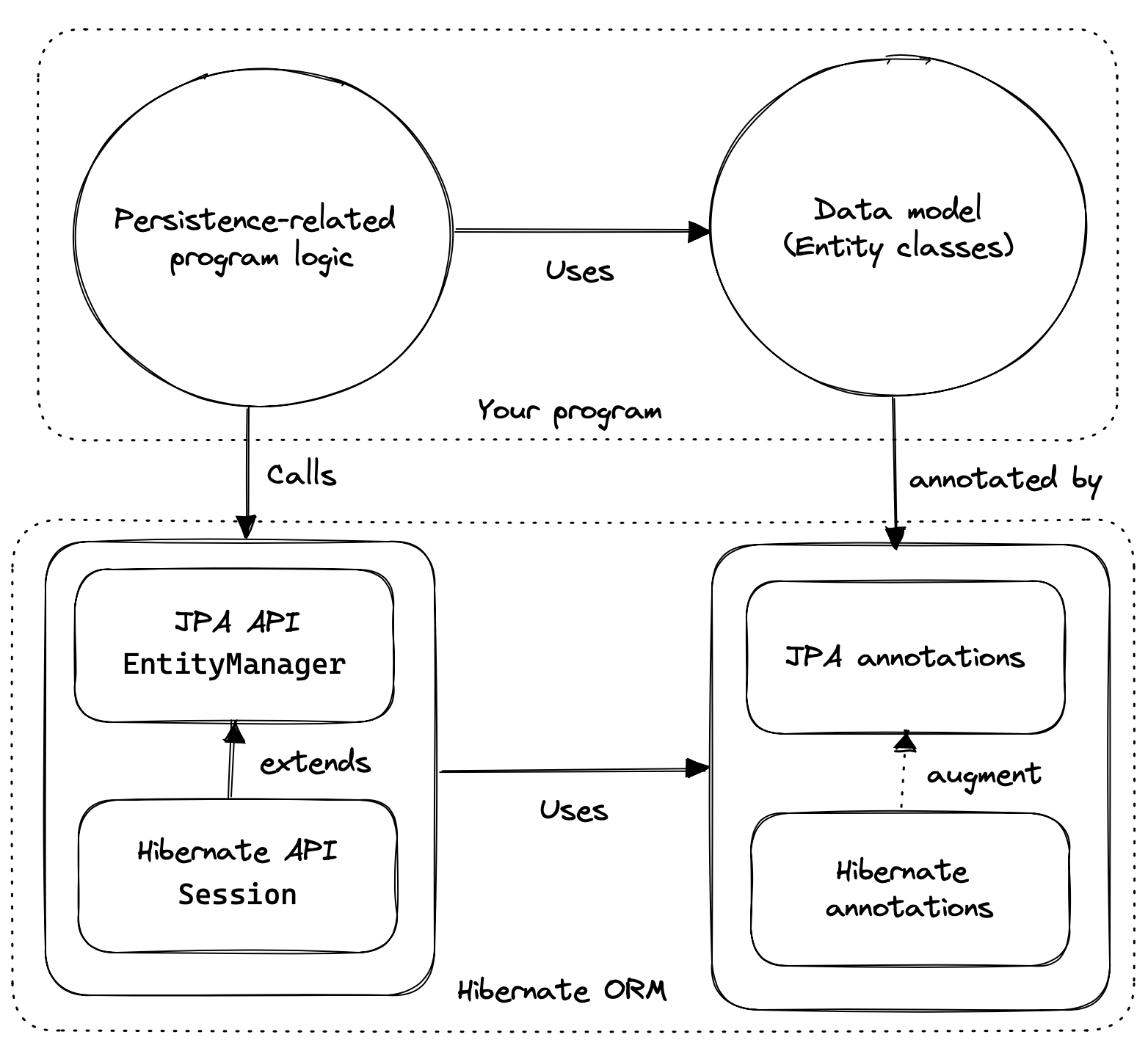
Spring Boot 애플리케이션이 시작될 때, 하나의 EntityManagerFactory를 생성해서 애플리케이션 전체에서 공유하며, 사용자가 DB의 데이터를 요청할때마다 EntityManagerFactory를 통해 세션(EntityManager)이 생성되고 응답을 반환하면 세션을 닫는다.

Spring Boot 애플리케이션에서 EntityManagerFactory를 생성되는 과정에서 DB 커넥션 정보와 함께 DataSource가 주입되고, EntityManager는 EntityManagerFactory를 통해 생성된다. 결국, EntityManager는 내부적으로 DataSource를 통하여 커넥션 풀로 부터 JDBC Connection 객체를 얻어 애플리케이션 서버와 데이터베이스 서버와 연결한다.
EntityManager는 트랜잭션 범위 내에서 트랜잭션을 마치기전까지 entity 객체와 DB 테이블간의 상태를 유지해야되므로 쓰레드간에 공유하면 절대 안된다.
직접적으로 EntityManager으로 트랜잭션을 다룬다면, EntityManager에서 getTransaction 메서드로 EntityTransaction 구현체를 가져와서 트랜잭션을 시작, 커밋, 롤백하는 작업을 수행할 수 있다.
EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("hello_jpa");
EntityManager entityManager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();
EntityTransaction transaction = entityManager.getTransaction();
try {
transaction.begin();
//do some work
Member member = new Member();
entityManager.persist(member);
transaction.commit();
}
catch (Exception e) {
if (transaction.isActive()) transaction.rollback();
throw e;
}
finally {
entityManager.close();
}
결국, EntityTransaction 구현체의 commit메서드는 내부적으로 JDBC Connection 구현체의 commit 메서드를 호출하여 트랜잭션을 커밋한다. JPA는 추상화 계층을 제공하지만 실제 데이터베이스와의 상호작용은 JDBC를 통해 이루어지기 때문에, 데이터베이스 트랜잭션 커밋은 JDBC Connection 구현체의 commit 메서드를 통해 수행된다.
트랜잭션을 마치면, close()메서드를 호출하여 세션(EntityManger)을 닫아야한다. 이는 내부적으로 Connection 구현체를 커넥션 풀에 반환한뒤, EntityManger 구현체가 관리하던 entity 객체가 1차 캐시(Persistence Context)에서 정리된다. 그리고 EntityManger 객체를 더이상 사용하지 않고 해제한다.
Persistence Context
Persistence Context란?
Entity는 인스턴화되어 메모리에 할당되고 해제되지만, DB의 테이블에는 entity가 반영된 상태가 지속되므로 지속성(persistence)이 있다.
이처럼 메모리의 일시적으로 저장되는 entity 객체와 디스크에 영구 저장되는 관계형 데이터베이스의 테이블간에 싱크를 맞추기 위해서, entity 객체의 지속성을 부여하기 위한 환경(persistence context)이 존재한다.
Persistence Context는 DB와 동기화할 entity 객체를 관리하기 위한것이며, 주요 역할은 다음과 같다.
- Entity 객체의 상태를 정의하고 변경하는 contexts를 제공하고, 세션(EntityManager)에서 persistence context를 사용하여 entity 객체 상태를 변경한다.
- DB와 동기화가 예정된 persistent 상태의 entity 객체를 임시적으로 저장하는 1차 캐시이다.
- entity 객체 상태 관리의 편의를 위한 entity 객체의 변경 사항울 자동으로 추적한다.
- 데이터베이스 서버 최소 접근을 위한 트랜잭션 지연 쓰기 등을 제공한다.
- 트랜잭션 동안 같은 데이터를 여러 번 읽을 때 항상 같은 entity 객체를 보장한다.
Persistence Context의 Entity 객체 상태 정의
위에서 Persistence Context는 1차 캐시라고 언급하였다. Entity의 상태는 1차 캐시에 저장된 적이 있거나, 저장중이거나, 저장된적이 없거나이다. 중요한것은 1차 캐시에는 persistent 상태의 entity만 저장한다는 것이다.
다음은 Entity 객체의 상태 변화 사이클이다. Entity는 transient, persistent, detached 3개의 상태를 갖는다.

- transient: 1차 캐시에 저장된적이 없는 entity 객체
- persistent: 1차 캐시에 저장중인 entity 객체
- detached : 1차 캐시에 저장되었다가 분리된 entity 객체
Persistence Context의 Operation
세션(EntityManager)의 Persistence Context의 작업에는 다음과 같이 여러 작업(operation)이 존재한다. 이러한 작업들은 SQL 쿼리로 변환되고 트랜잭션이 커밋 되면 실행된다.
public interface EntityManager extends AutoCloseable {
void persist(Object var1);
<T> T merge(T var1);
void remove(Object var1);
void clear();
void flush();
//...
}
- persist(entity): transient 상태의 entity를 persistent 상태로 만들고 추후 insert SQL 문이 실행되도록 스케줄링한다.
- remove(entity): persistent 상태의 entity를 transient 상태로 만들고 추후 delete SQL 문이 실행되도록 스케줄링한다.
- merge(entity): 동일한 persistent 상태의 entity가 저장되어있다면, 인자값으로 받은 detached 상태의 entity로 복사를 한다. 저장되어있지 않다면, 새로 생성한 persistent 상태의 entity를 반환한다.
- clear(): persistent 상태의 entity를 비우고 모든 entity를 detached 상태로 변경한다.
- flush(): 즉시, 세션(EntityManager)에서 persistent 상태의 entity 객체에 대한 변경 사항을 감지하고, SQL문(insert, update, delete)을 실행시켜 세션의 상태와 데이터베이스의 상태와 동기화한다. JPA에서 트랜잭션 커밋을 하면 flush 메서드가 자동으로 호출된다.
1차 캐시
Persistence Context는 데이터베이스의 테이블에 영구적으로 반영될 entity 인스턴스를 저장하는 1차 캐시이다. 1차 캐시는 Entity의 타입과 PK (@Id)으로 식별하여 entity 인스턴스를 저장된다.
EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("hello_jpa");
EntityManager entityManager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();
EntityTransaction transaction = entityManager.getTransaction();
try {
transaction.begin();
Member member = new Member();
member.setId(1L);
member.setName("John Park");
// 1차 캐시에 저장됨
entityManager.persist(member);
transaction.commit();
}
catch (Exception e) {
if (transaction.isActive()) transaction.rollback();
throw e;
}
finally {
entityManager.close();
}
EntityManger 구현체를 통하여 persist 메서드를 실행시켜 member entity를 Persistence Context(1차 캐시)에 저장하였다. 이러한 entity의 상태를 persistent라고 한다. 이는 영구적으로 DB에 반영할 객체인것이며, 아직 DB에 반영되지 않은 상태이다. 허나, DB 반영 이후에도 세션(EntityManger)을 닫지(close()) 않으면 1차 캐시에 남아있다.

1차 캐시에서 조회
persist 메서드가 실행되어 member entity 1차 캐시에 저장 되고, 이후 find 메서드를 실행시키면 1차 캐시에서 조회할 수 있다.
EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("hello_jpa");
EntityManager entityManager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();
EntityTransaction transaction = entityManager.getTransaction();
try {
transaction.begin();
Member member = new Member();
member.setId(1L);
member.setName("John Park");
// 1차 캐시에 저장됨
entityManager.persist(member);
// 1차 캐시에서 조회
Member findMember = entityManager.find(Member.class, 1);
transaction.commit();
}
catch (Exception e) {
if (transaction.isActive()) transaction.rollback();
throw e;
}
finally {
entityManager.close();
}

DB에서 조회
동일한 트랜잭션에서 같은 entity를 여러 번 조회할때의 시나리오이다. 이전에 member entity 객체와 매핑되는member 테이블의 row가 DB에 저장되었다고 가정하자.
첫번째 조회때는 찾는 entity가 1차 캐시에 없으면, 데이터베이스 테이블에서 데이터를 가져와서 entity를 1차 캐시에 갱신한 후에 entity를 반환한다. 이후에는 데이터베이스가 아닌 1차 캐시에서 entity 인스턴스를 반환받는다.
EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("hello_jpa");
EntityManager entityManager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();
EntityTransaction transaction = entityManager.getTransaction();
try {
transaction.begin();
// DB에서 조회
Member findMember1 = entityManager.find(Member.class, 1);
// 1차 캐시에서 조회
Member findMember2 = entityManager.find(Member.class, 1);
transaction.commit();
}
catch (Exception e) {
if (transaction.isActive()) transaction.rollback();
throw e;
}
finally {
entityManager.close();
}
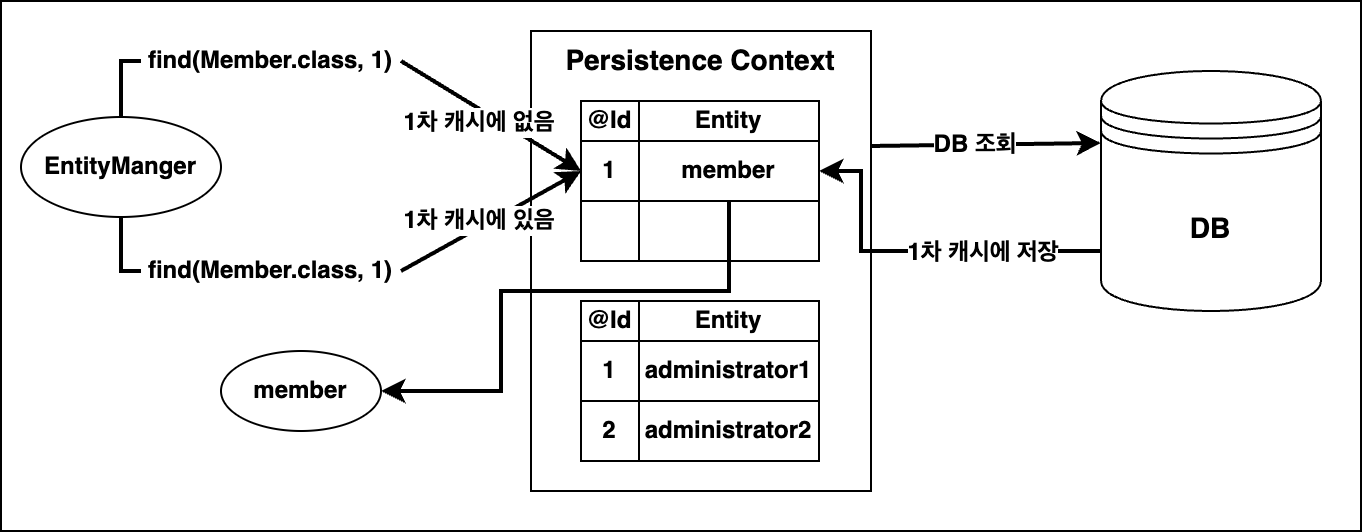
Persistence Context는 DB 접근 최적화 효과도 있겠지만, 트랜잭션을 마쳐서 세션(EntityManager)이 닫히면 Persistence Context에서 EntityManager의해 관리되던 enttity 객체가 제거되기 때문에 속도 측면에서의 약간의 이점만 있을뿐이다.
Persistent 상태의 Entity 동일성 조회
다음 코드에서 트랜잭션 내애서 Persistence Context에 저장되어 있는 entity 객체의 주소가 동일한지 == 연산자로 확인 할 수 있다. 트랜잭션 동안에 같은 entity 여러번 조회해보면 동일한 entity 객체를 반환하는 것을 알수 있다.
EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("hello_jpa");
EntityManager entityManager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();
EntityTransaction transaction = entityManager.getTransaction();
try {
transaction.begin();
// DB에서 조회
Member findMember1 = entityManager.find(Member.class, 1);
// 1차 캐시에서 조회
Member findMember2 = entityManager.find(Member.class, 1);
//동일성 비교 true
System.out.println(findMember1 == findMember2);
transaction.commit();
}
catch (Exception e) {
if (transaction.isActive()) transaction.rollback();
throw e;
}
finally {
entityManager.close();
}
위의 결과는 애플리케이션 내에서 1차 캐시로 데이터베이스의 반복 가능한 읽기(REPEATABLE READ) 등급의 트랜잭션 격리 수준을 제공하는 것이다. 이는 트랜잭션 동안 같은 데이터를 여러 번 읽을 때 항상 동일한 결과를 보장하는 격리 수준이다.
트랜잭션을 지원하는 쓰기 지연 (Transactional Write-Behind)
쓰기 지연(Transactional Write-Behind)은 트랜잭션이 커밋(commit)되기 전까지 데이터베이스에 대한 쓰기 작업(INSERT SQL)을 지연시키고, 트랜잭션이 성공적으로 커밋된 후에 한 번에 데이터를 반영하는 방식이다.
EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("hello_jpa");
EntityManager entityManager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();
// EntityManager는 데이터 변경시 트랜잭션을 시작해야 한다.
EntityTransaction transaction = entityManager.getTransaction();
transaction.begin(); // 트랜잭션 시작
Member memberA = new Member();
member.setId(1L);
member.setName("John Park");
Member memberB = new Member();
member.setId(2L);
member.setName("James");
em.persist(memberA);
em.persist(memberB);
// 여기까지 INSERT SQL을 데이터베이스에 보내지 않는다.
// 커밋하는 순간 데이터베이스에 INSERT SQL을 보낸다.
transaction.commit(); // [트랜잭션] 커밋
위의 코드에서 트랙잭션 내에 entity 객체 memberA와 memberB에 대한 쓰기 작업(persist)이 두개가 존재한다. persist메서드가 실행되어 memberA에 대한 INSERT SQL을 생성하고 persistence context 내의 쓰기 지연 SQL 저장소(Write-Behind Buffer)에 적재된다. 그 다음 동일한 방식으로 memberB에 대한 INSERT SQL문이 적재된다.
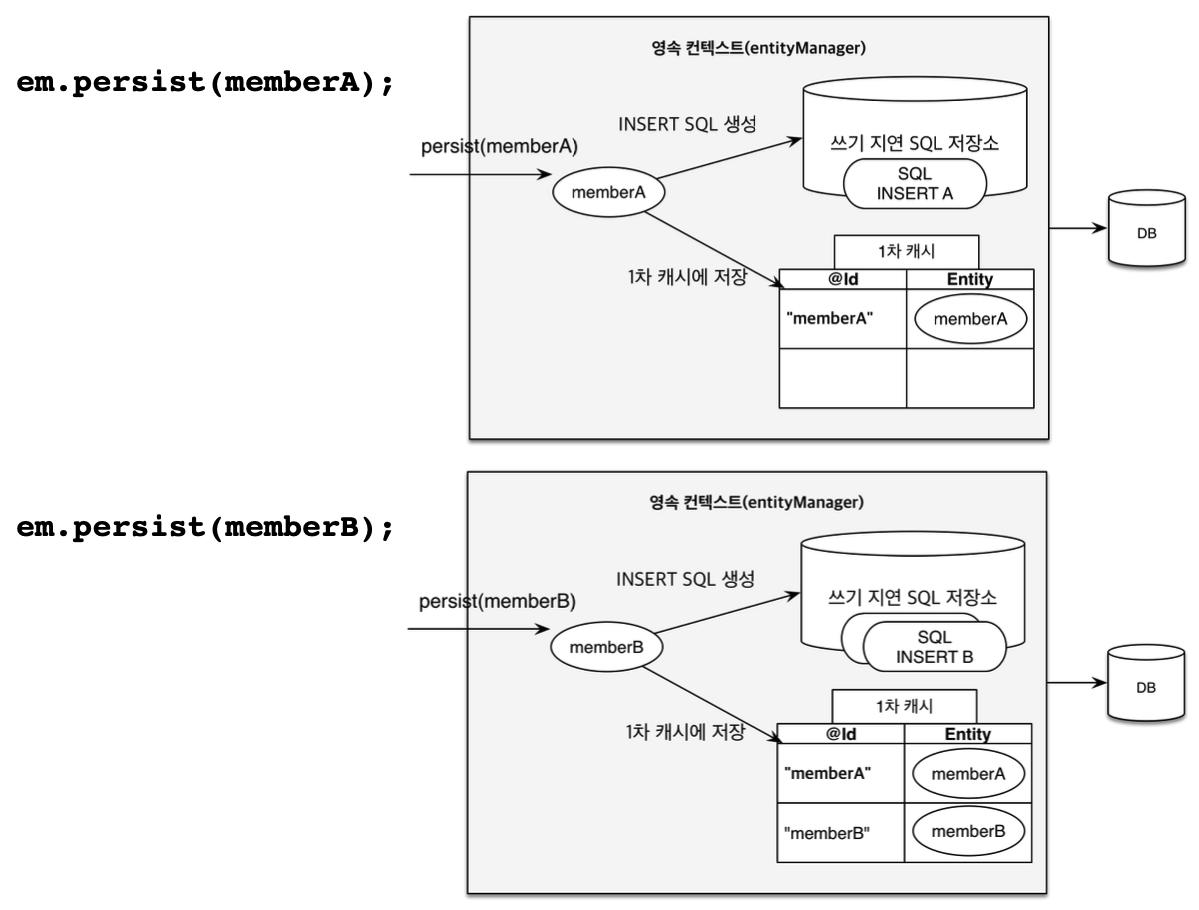
이후, EntityTransaction 구현체의 commit()이 호출되면, JPA 구현체는 자동으로 flush()를 호출하여, 즉각적으로 세션(EntityManger)에서 트랜잭션 범위에서 entity 객체의 모든 변경 사항을 포함해서 쓰기 지연 SQL 저장소의 SQL문을 데이터베이스에 전달한다. 그런 다음 JDBC Connection 구현체의 commit()를 호출되어 데이터베이스 트랜잭션을 커밋하여 변경 사항을 확정한다.

만일, 애플리케이션 서버에서 트랜잭션 내의 여러 SQL문을 데이터베이스 서버에 각각 전달하여 실행하게 되면, 여러 차례 데이터베이스와 왕복해야하므로 네트워크 비용(시간, 돈)이 발생한다. 그러므로 Persistence Context의 버퍼에 트랜잭션 내의 여러 SQL 문을 적재했다가 한번에 데이터 베이스 서버에 전달하면, 데이터베이스와의 네트워크 왕복 횟수를 줄일 수 있다.
Dirty Checking (변경 감지)
Persistence Context는 entity 객체의 변경 사항을 자동으로 감지(dirty checking)한다. 그래서 아래의 코드처럼 memberA의 필드를 멤버 변수만 변경해주어도, EntityTransaction 구현체의 commit 메서드 실행 이후에 변경된 entity 객체를 자동으로 인지하고 SQL로 변환되서 DB에 반영된다.
EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("hello_jpa");
EntityManager entityManager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();
EntityTransaction transaction = entityManager.getTransaction();
transaction.begin(); // 트랜잭션 시작
// 영속 엔티티 조회
Member memberA = entityManager.find(Member.class, "memberA");
// 영속 엔티티 데이터 수정
memberA.setUsername("hi");
memberA.setAge(10);
//em.update(member) 이런 코드가 있어야 하지 않을까?
transaction.commit(); // 트랜잭션 커밋
Persistence Context에서 entity 객체의 변경 사항에 대해서 자동으로 감지하기 위해서, 1차 캐시에 저장된 entity 객체와 entity 객체의 스냅샷이 존재한다. 이 스냅샷은 persistence context에 entity 객체가 처음으로 저장된 상태의 복사본이다. 이는 entity 객체가 처음으로 영속화(persist)되거나 데이터베이스에서 로드될 때 생성된 것이다. 스냅샷을 저장된 entity 객체를 갱신하지 않는다. 세션의 트랜잭션 범위 내에서만 쓰이기 때문에 지속적인 갱신은 불필요한 오버헤드를 발생시킨다.
Entity 객체의 필드 변경 이후에, EntityTransaction 구현체의 commit 메서드 실행되면 내부적으로 flush 메서드가 호출된다. 그러면 기존의 1차 캐시에 저장된 entity 객체와 저장된 스냅샷을 비교하여, 두 상태가 다르면 entity 객체가 변경된 것으로 감지하고 적절한 SQL UPDATE 문이 생성되어 쓰기 지연 SQL 저장소(Write-Behind Buffer)에 적재된다. 그 다음 SQL 문을 실행하도록 데이터베이스에 전송되고, JDBC Connection 구현체의 commit()가 호출되어, 데이터베이스에서 트랜잭션이 커밋되고 변경 사항을 반영한다.
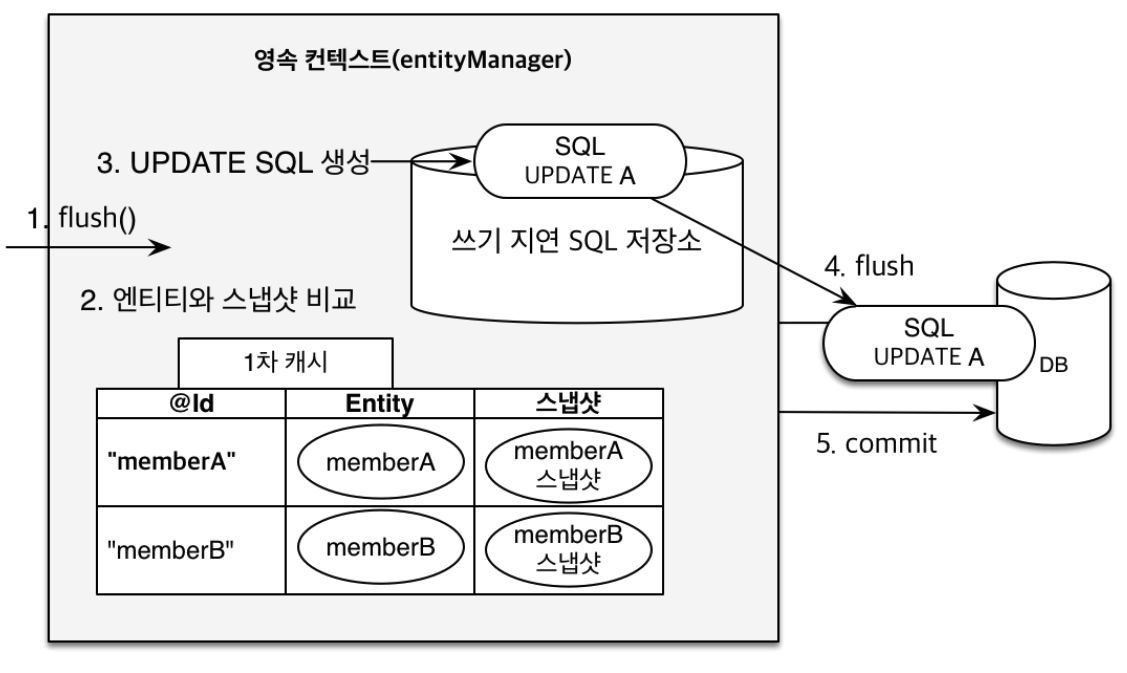
Persistence Context는 entity 객체의 변경 사항을 자동으로 감지하므로 세션에서 트랜잭션 커밋 시점에 자동으로 데이터베이스에 반영될수 있다. 이는 개발자가 entity의 변경 사항에 대해 직접 관리할 필요 없이 JPA가 자동으로 처리해 주어 개발 편의성을 높여준다.
JPA를 사용한 애플리케이션과 데이터베이스와의 상호작용
모든 entity 객체는 EntityManager을 통해 영속성 컨텍스트(persistence context)에 저장되고 관리된다. 세션 역할의 EntityManager는 트랜잭션 범위 내에서 영속성 컨텍스트(persistence context)와 상호작용하여 entity 객체 상태를 관리하고 EntityTransaction을 통해 트랜잭션을 수행한다. 트랜잭션을 커밋하면, 영속성 컨텍스트에 저장된 entity 객체(변경 사항 포함)에 대한 SQL문이 데이터베이스에 반영된다. 이로써, 자바 객체와 데이터베이스 간의 일관성을 유지하면서 상호작용 할 수 있다. 그리하여, 객체 지향 중심인 자바 애플리케이션과 SQL 중심인 데이터베이스간에 부분도 객체 중심적으로 개발이 가능하다.
참고자료
- An Introduction to Hibernate 6
- 자바 ORM 표준 JPA 프로그래밍 - 기본편